Jewelry business AML compliant – RAHN CASE STUDY ISSUE NO.14-2022
How to get your Jewelry business AML compliant – Deep dive into the Kruger Rand Business
Rahn Consolidated (Pty) Ltd’s (“Rahn Consolidated”) articles and case studies are aimed at socialising, climatising, creating awareness and cautioning economic participants on regarding economic crime schemes. The focus will inter alia be on the investigations around Jewelry business AML compliant, risks, reporting and most importantly, its regulatory compliance. The term “Economic crime schemes” are often used interchangeably with “Financial Crime”.
For the purpose of ensuring all readers are kept in the loop, Rahn Consolidated will make use of both terms. Rahn Consolidated being at the forefront of deterring Financial Crime through compliance will focus primarily on the compliance of regarding Financial Crime and ensuring fines by way of administrative sanctions that fines are mitigated as much as possible.

Issue No.14 focuses on Reporting Institutions particularly relating to Kruger Rand dealing. This industry, dealing primarily in money in the form of Kruger Rands could be cash intensive and therefore easily susceptible to money laundering.
South Africa has specifically applied reporting obligations on Kruger Rand dealers, which are not classified as Accountable Institutions (AI) under the Financial Intelligence Centre Act but rather Reporting Institutions (RI).
This issue highlights risks affecting Kruger Rand dealers when it comes to money laundering.
Enjoy the Read!
Item 2 of Schedule 3 of the Financial Intelligence Centre (FIC) Act identifies a person who carries on the business of dealing in Kruger Rands as a Reporting Institutions (RI) .
The FIC views “a person who carries on the business of dealing in Kruger Rands” to be any person who, as a regular feature of his/her business, deals in jewellery, ornaments, watches or other objects that contain Kruger Rands irrespective of the value of the turnover of the Kruger Rand dealer. For purposes of this article, “dealer” is therefore regarded as someone who trades in Kruger Rands.
- Some businesses including jewellers are buying Kruger Rands and using these to manufacture jewellery, ornaments and watches that contain the original Kruger Rands.
- The inclusion of a Kruger rand in another object such as a piece of jewellery, ornament, watches etc. does not alter the intrinsic nature of Kruger Rand.
- The FIC therefore views any person who, as a regular feature of his/her business, deals in jewellery, ornaments, watches or other objects that contain Kruger Rands to be a dealer in Kruger Rands.
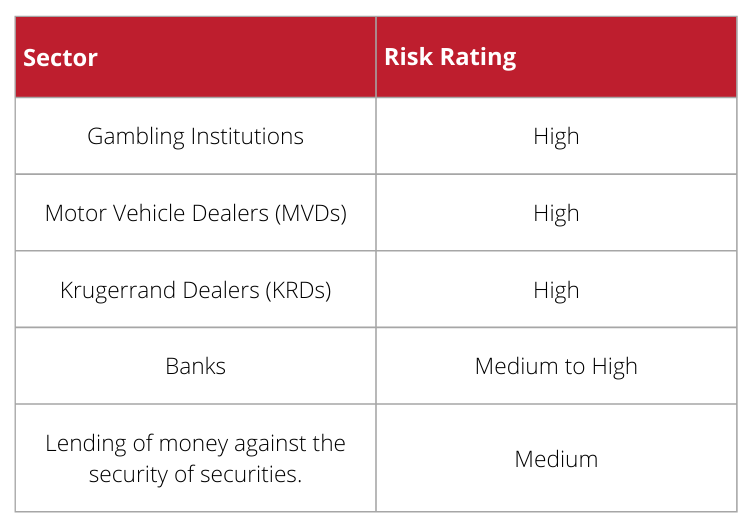
FIC Kruger rands guide
Based on this table, Kruger Rands are rated high-risk and as such reporting controls need to be embedded in a business to ensure that the risks are mitigated:
FATF Mutual Evaluation
The reporting obligations concerning RI are as follows:
- Cash Threshold Reporting
Kruger Rand dealers are required to report cash transactions above the prescribed threshold in terms of section 28 of the FIC Act.
- Suspicious and Unusual Transaction Reporting
Section 29 of the FIC Act requires that any person, who carries on a business, is in charge of a business, manages a business, or is employed by a business, must report suspicious or unusual transactions to the FIC. This reporting obligation is
applicable to a person who carries on the business of dealing Kruger Rands. About 2.63% of the total 2021 reporting eminated from the Kruger Rand dealers while the bulk of the reporting eminates from Banks (82%).
Considering the FATF Mutual Evaluation’ sector risk rating, it is evident that the this industry needs to increase awareness to ensure that it is fully compliant. Rahn Consolidated can assist in implementing the correct reporting capabilities.
ML/TPF Risks Example: Kruger Rand Dealer

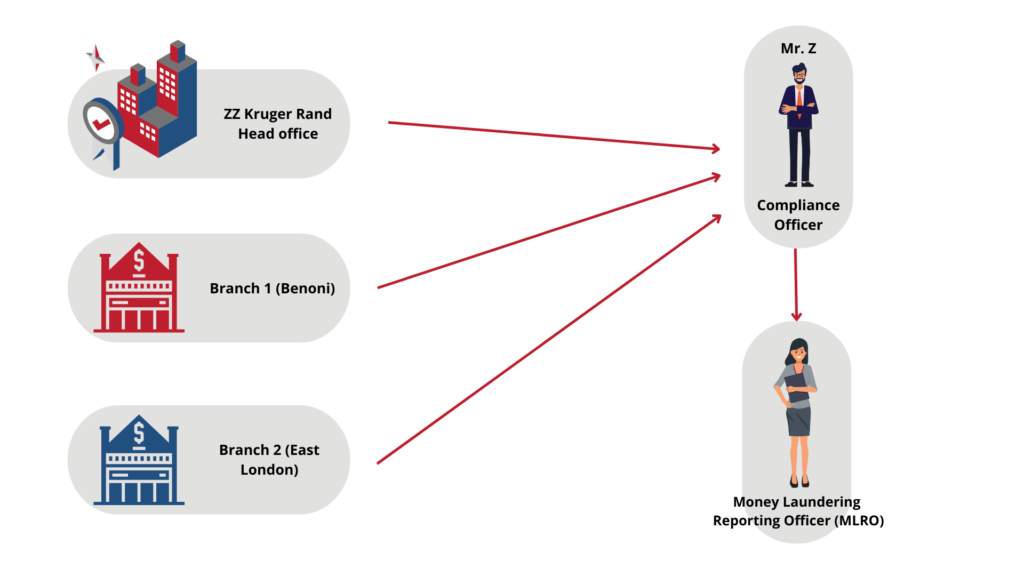
It is important to note that the head office and branches are separate reporting institutions and can be registered separately by the reporting officer responsible for the head office or branch. This also applies to franchises. The registration platform also allows for an instance where one reporting officer is appointed for all branches. A Kruger Rand dealer has one head office and three branches in South Africa. Mr Z is the reporting officer responsible for the head office and all three branches.
It is important to note that only Mr Z can register the head office and branches and only Mr Z will have access to the registration and reporting information. It is furthermore important to note that reporting to the Centre follows the registration structure of the accountable institution. Multiple Money Laundering Reporting Officer (MLRO) can be added per registration structure i.e. per head office and per branch. If the MLRO is registered at branch level, he/she can only see reporting information of that particular branch.
Example of Kruger Rand Dealers registration